#5540
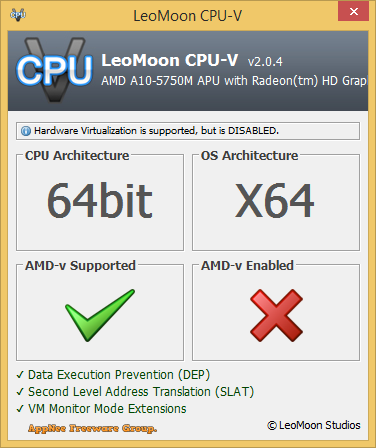
The most direct application of virtualization technology (VT) is to run virtual machines in a system. If the CPU supports the VT, you can install virtual machines on your system; on the other hand, if your CPU does not support VT, then you will not be able to use virtual machine applications. That also means it's time to change your computer. To enable VT: Restart computer to enter the BIOS; Find the corresponding VT option; Adjust the setting from "Disable" to "Enable"; Save and restart.
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
#5539
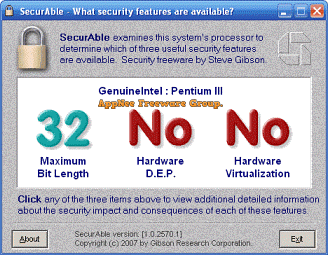
To use the virtualization technologies (such as virtual machine) with certain combinations of some version of Windows and some model of CPU, you need to check to see if your computer supports the hardware level virtualization capabilities. SecurAble is a CPU security features detection tool, can check if your processor chip supports 64-bit, VT (Virtualization Technology), and hardware data execution protection (Hardware D.E.P.) these three state-of-the-art features that are related to the overall security of a system.
Loading...
#5013

VMware vSphere (formerly VMware Infrastructure 4) is currently the world's leading server virtualization solution (including a series of products, of which ESXi and vCenter Server are used a lot), also the most stable and reliable cloud computing virtualization platform, developed by VMware. It can separate applications and operating systems from the underlying hardware, so as to simplify IT operations.
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
#3816
When a virtual machine solution is mentioned, most of use probably think of the celebrated VMware Workstation (which always stays ahead of the VirtualBox from Germany on performance and compatibility). Compared with VMware Workstation Pro, VMware Workstation Player (AKA: Player Pro, VMware Player for short) is more lightweight in both file size and function (can be seen as the simplified edition of VMware Workstation Pro), runs faster, and is free and more suitable for personal, home or non-commercial use.

Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
#3397

QEMU (short for Quick Emulator) is a free and open-source processor emulator widely used on GNU/Linux platform, written by Fabrice Bellard from France. It primarily converts the binary code written for a specific processor to another through a special 'recompiler', so as to realize the OS virtualization.
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...